- Published on
What is a VPN?
VPN
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network.
Imagine that you want to connect two or more computers to a network and that network is securely accessible only by your computers. One way to do that is by setting up your own exclusive physical cables and networking devices in geographical locations of all your computers.
Alternatively, a VPN lets you do that without an expensive physical setup:
- Virtual: Connection between your computing devices is virtual on existing physical network.
- Private: Data transfer on connection is encrypted and hence private, preventing others from seeing your data or browsing activities.
- Network: Your device and VPN server forms a network. This network can be extended to connect many devices to form a virtual private network.
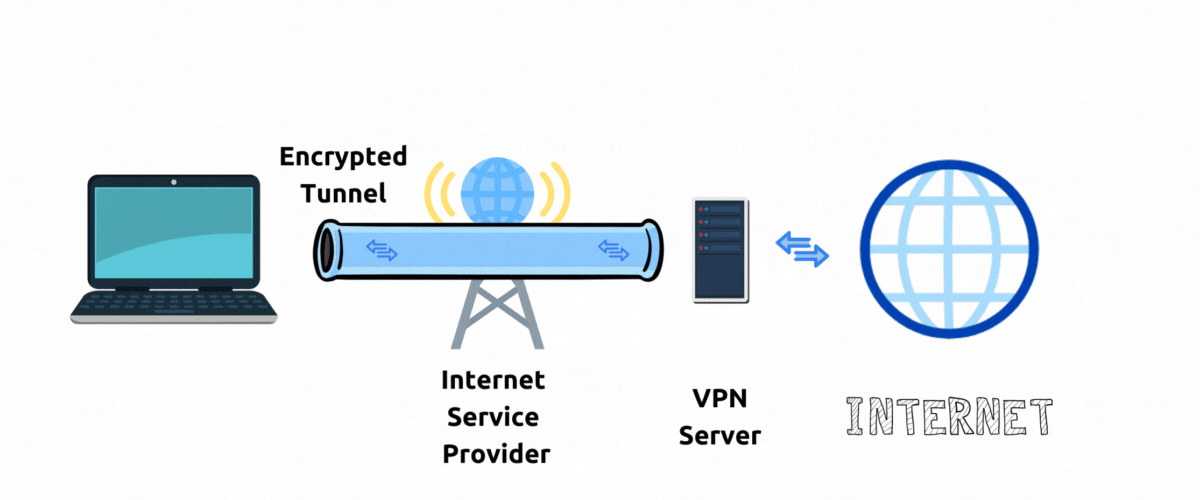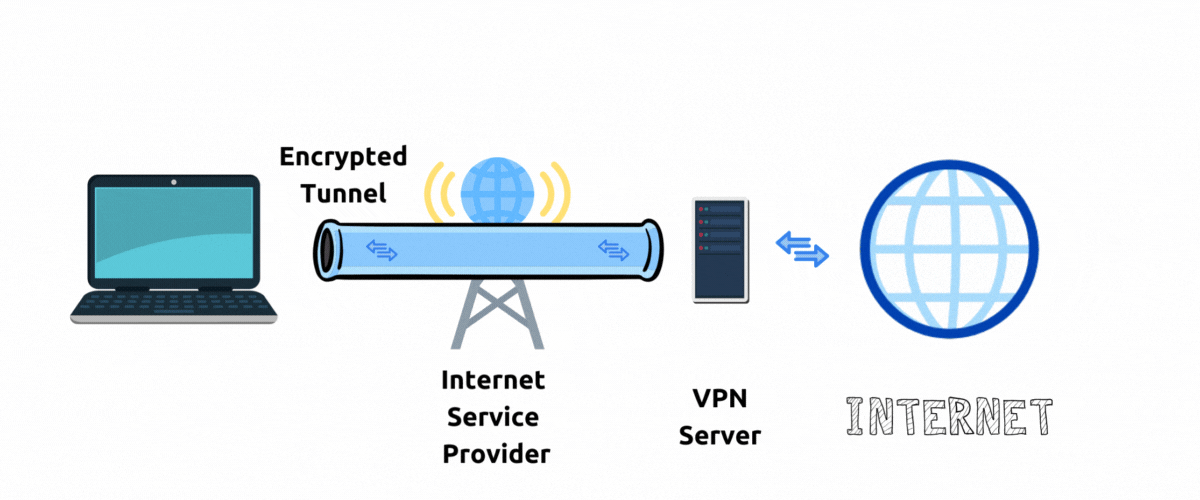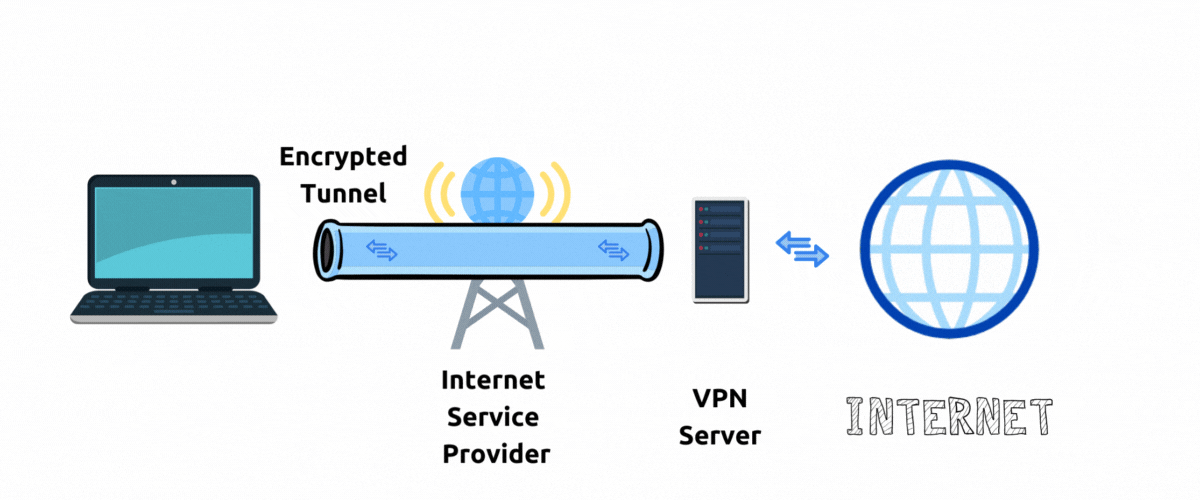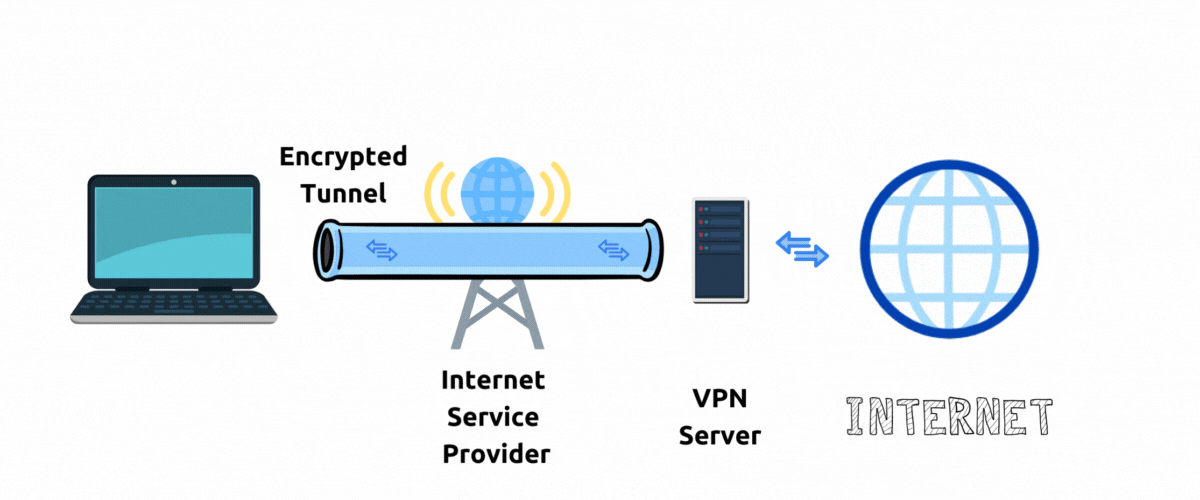
A private encrypted connection between your device and VPN server is also called a point-to-point Tunnel.
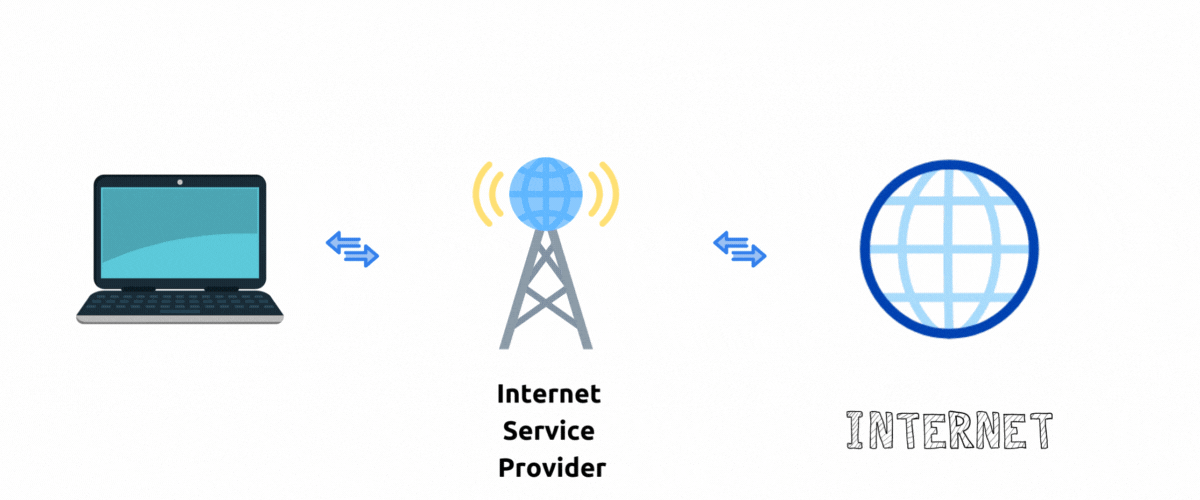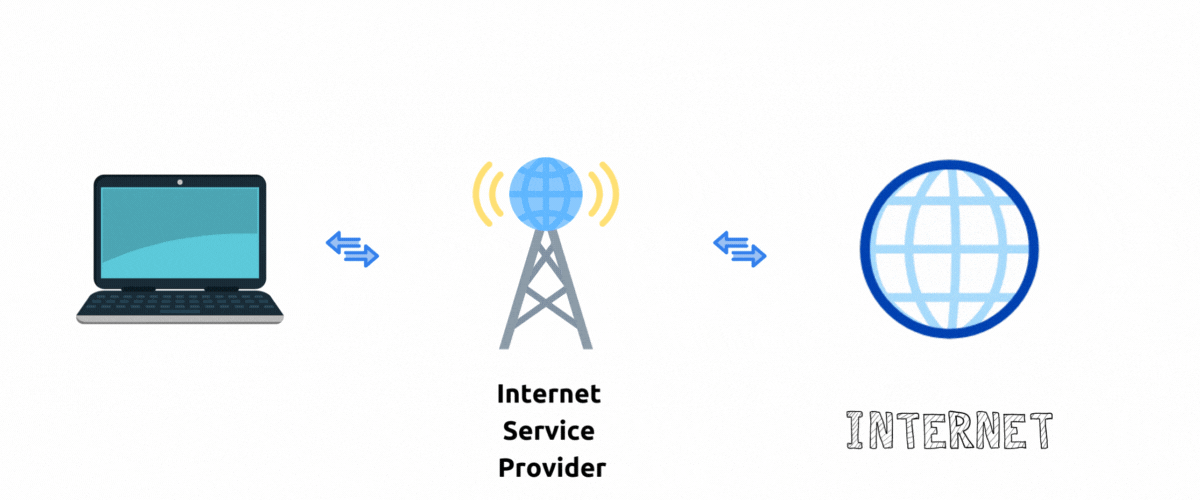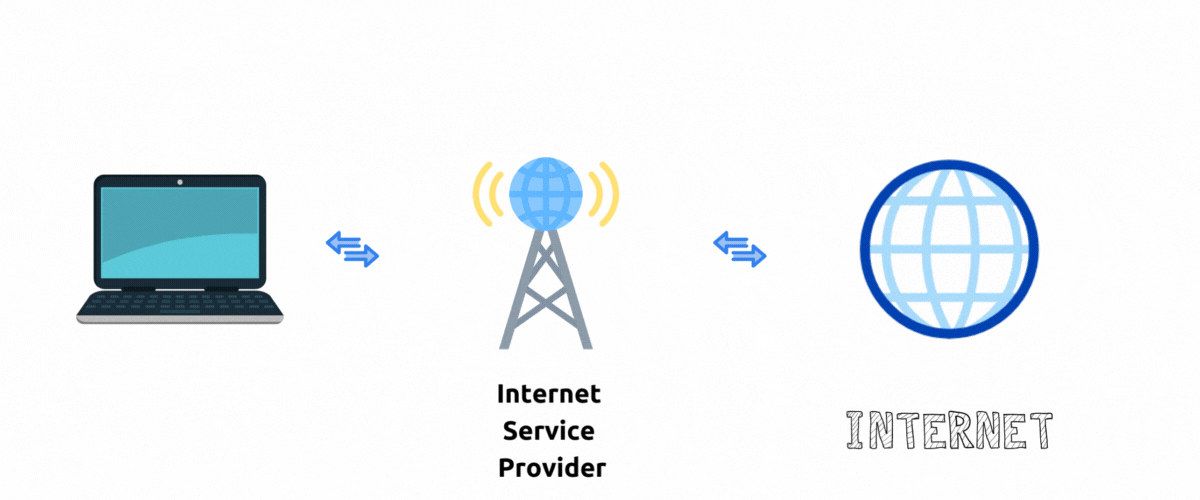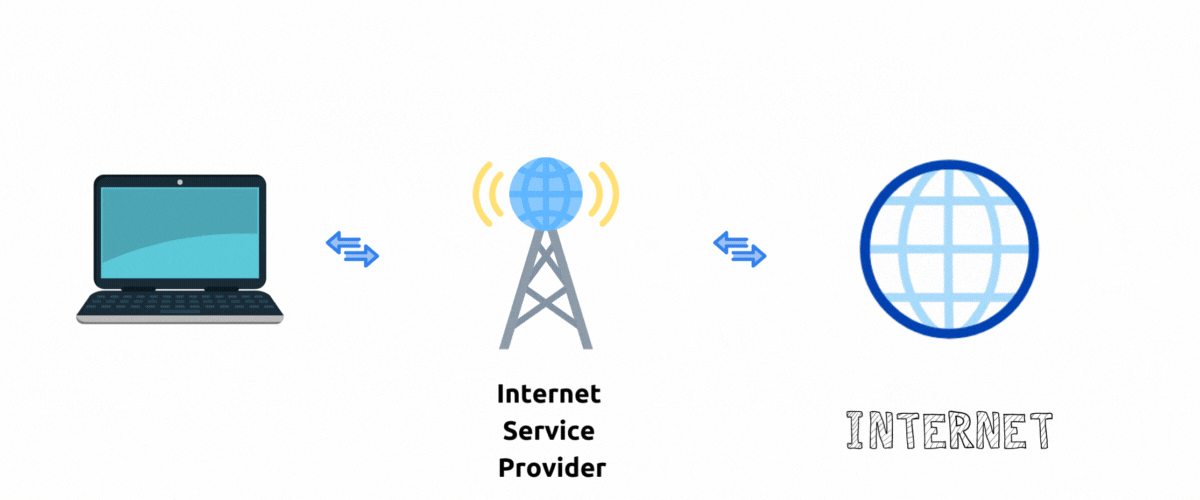
Without VPN
When you visit websites your internet traffic goes through an Internet service provider to the destination website. To the website server it appears that your traffic is originating from IP addresses (and corresponding location) that ISP assigned to you.
With VPN
With VPN your network traffic goes through an encrypted tunnel to a VPN server and then to public internet before arriving at the destination website server.
To the website server it appears that your traffic is originating from the location and IP address of a VPN server. In this way VPN server hides your actual IP address and hides your physical location. In this setup a VPN Server acts as a "proxy" to internet.
VPN enables you to access internet from a different geographical location by choosing a VPN server in a different city, state, or country!